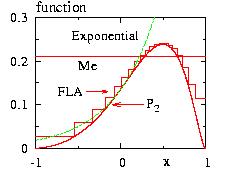
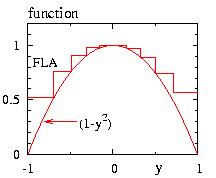
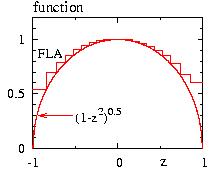
- Figure: The probability P(x) and the test function f(x) for various algorithms.
FLA=Fast Linear Algorithm
Ex =Exponential
Me =Metropolis
P2=P(x) with h=2
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
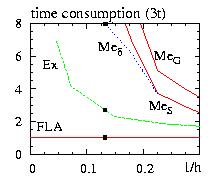
- Figure: comparison of the time of simulation for various algorithms
for the stacked triangular antiferromagnetic lattices.
The critical temperature is shown by the squares
- FLA=Fast Linear Algorithm
- Ex =Exponential
- MeG =Metropolis standard using NS Gaussian random numbers.
- MeS =Metropolis, angles, sinNS-2(theta) ... are chosen from
a sinus distribution and the rejection method
- Med =like MeS but the first angle is constrained
to be around the old spin (0 < first angle < d).
|
|
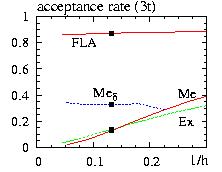
- Figure: comparison of the rate of simulation for various algorithms
for the stacked triangular antiferromagnetic lattices.
The critical temperature is shown by the squares
- FLA=Fast Linear Algorithm
- Ex =Exponential
- MeG =Metropolis standard using NS Gaussian random numbers.
- MeS =Metropolis, angles, sinNS-2(theta) ... are chosen from
a sinus distribution and the rejection method
- Med =like MeS but the first angle is constrained
to be around the old spin (0 < first angle < d).
|
|




