|
Damien LOISON Gnuplot Links QIPGraphÓ :
C++ and Excel Interface for gnuplot |
Rectangles,
circles, and background |
Examples
“Clean examples”. I tried to be as simple as possible to understand the main features.
One of the most useful shortcut is to press space to set the focus of the command window from the plot window
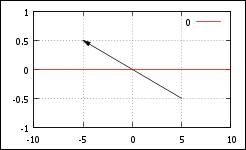
Arrows
# number from-to
head type
style
set arrow 1 from 5,-0.5 to -5,0.5
head filled size screen 0.03,15 linewidth 1 linetype rgb "black"
# set arrow 1 to 1,1 # change head
p 0
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/arrowstyle.html
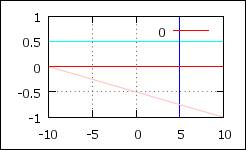
Lines
#
from-to
type
color
set arrow 2 from graph 0, first 0.5 to graph 1, first 0.5 nohead linewidth 1 linetype rgb
"cyan" # horizontal
set arrow 3 from 5,-1 to 5,1 nohead linewidth 1 linetype rgb "blue"
# vertical
set arrow 4 from graph 0,0.5 to graph 1,0 nohead
# from graph coordinates
p 0
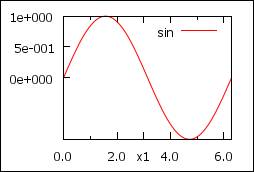
Axes
set xtic 2
# every 2
set ytics 0,0.5
# from 0, every 0.5
set ytics nomirror
# do not show tics at the right
set xtics add("x1" 3)
# add one tic “x1” at 3
set format x "%.2f"
# 2 decimals for x
set format y "%1.0e"
# exp format for y
set mxtics 2
# minor x tics frequency = 2
p
[0:2*pi] sin(x) t "sin"
# set xtics ("NE" 72.0,
"S" 42.0, "Downtown" 12.0, "Suburbs" 122.0) # define xtics
on axe x
# set format x ""
# no number for x axis
set zeroaxis
# plot axis , xzeroaxis, yzeroaxis
Axes with arrows
set border 3
# border left + bottom
set tics nomirror
# no tics on right and top
set arrow 1 from graph 1,0 to graph 1.09,0 size screen
0.02,15,60 filled # axe x + type
arrow
set arrow 2 from graph 0,1 to graph 0,1.09 size screen
0.02,15,60 filled # axe y + type
arrow
set tmargin at screen 0.90
# otherwise margin calculated automatically
set rmargin at screen 0.90
#
and not sure to see arrows
p cos(x)
Axe time
set xdata time
# set axis time format
set format x "%d/%m/%y %H:%M:%S"
# display
set xtics 5*24*60*60 rotate by -60
in
# frequency in seconds: 5 days, rotate -60 degres,
inside tics
set xrange
["01/06/2003":"21/06/2003"]
# time does not see to work
p cos(x)
# time = seconds from 01 january 2000
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/timedat.html
Two y axes
set ytics nomirror
# not same tics left and right
set ytics -1, 0.5 textcolor
rgb "red"
# left tics from -1 with 0.5
interval
set y2tics 0, 0.2 textcolor rgb "green" # right
tics from 0 with 0.2 interval
set y2range[0:1]
# right axis range
p [0:2*pi] sin(x) lt rgb "red" axis x1y1,sin(x)**2 lt
rgb "green" axis x1y2 # plot and choose color of
figures
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/multiaxis.html
Axes label
set xlabel "x label" offset
graph 0.4,0.05
# standard: center, move to the right
set ylabel "y label" rotate
by 90 offset graph 0,0.4 # standard center, move to the top
set ytics 0.5
# 0.5 interval
p cos(x)
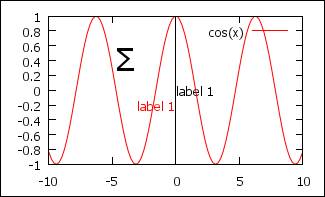
Label
set label 1 "label 1" at 0,0 left
# label from
set label 2 "label 1" at 0,-0.2 right textcolor rgb
"red" # label
to
set arrow 2 from first 0, graph 0 to first 0, graph 1 nohead # to see the diff
set label "S" at graph 0.3,0.8 center font
"Symbol,24" # sigma
"Time-Roman,12"
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/enhanced_utf8.html
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/textrotate.html
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/textcolor.html
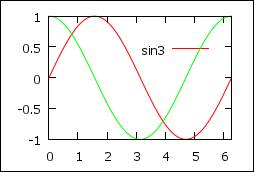
Legend
set key off
# no legend
set key 4,0.6 left
# legend from (4,0.6)
p [0:2*pi] sin(x) t sprintf("sin%d",3),cos(x) notitle
# using C format, no title for second function
You can choose to put the legend outside:
set key below
# below the figure
set key above
# above the figure
set key outside right
#
outside right bottom
set key box lt rgb
"black" lw 1
# box around legend
# set key spacing 0.7
# reduce spacing between legend, but pb with box
p
[0:2*pi] sin(x) t “sin”,cos(x)
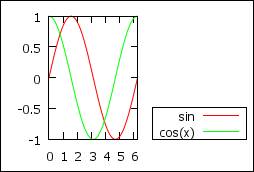
set key invert
# invert order of legend = same if invert order of plot
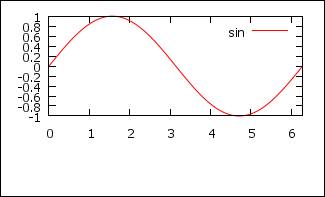
Margin
set bmargin 5
# bottom, can be “l”, “r” or “t”,
useful to align multiplots
p
[0:2*pi] sin(x) t "sin"
Multiplot 1
set multiplot layout 2,1 # two rows,
1 col
set lmargin 6
# to aligne the two figures
p x**2
set lmargin 6
# to aligne the two figures
p x**3
unset multiplot
# stop multiplot mode, otherwise plot new
curves on the top
Multiplot 2: insert
set multiplot
# enter multiplot mode
p x**4
set rmargin at screen 0.70 # right margin at 0.7 in the screen
set lmargin at screen 0.30 # left margin at 0.3
set bmargin at screen 0.40 # bottom margin at 0.4
set tmargin at screen 0.80 # top margin at 0.8
p x**2
# plot insert
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/multiplt.html
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/layout.html
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/margins.html
3D plot
set ticslevel 0.
# z start at 0, (default=0.5)
set isosample 40,40
# more accurate surface (default 10)
set hidden3d
# do not show hidden surface
set pm3d at s
# s = normal, b = surface
set palette rgbformulae 33,13,10 # change color
set border 4095
# to see all borders until the top
# set grid z
# if you need grid for z
sp [0:2*pi] [0:2*pi] sin(x)*cos(y)
set pm3d map
# map 3d to 2d
set pm3d s
# go back to normal surface
set view
# 2d to 3d
sp [0:2*pi] [0:2*pi] sin(x)*cos(y) #
get the first figure in 3d
Candelstick
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/candlesticks.html
Steps
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/steps.html
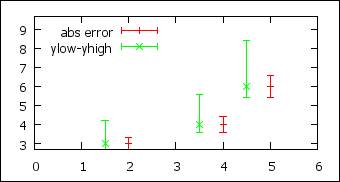
Error bars
set key left
# legend at
the left of the graph
set xrange [0:6]
p 'data1.dat' u 1:2:($2/10) w e t "abs error"\
,'data1.dat' u ($1-0.5):2:($2*9/10):($2*14/10) w e t "ylow-yhigh" # x:y:y_low:y_up
Bar chart / histogram 1
set boxwidth 0.9 relative
# size relative to the default
set style data histograms
# bar
set style fill solid 1.0 border -1 # with
border , see help border for options
p 'data1.dat' u 2,'' u 3
# show 2 bars for each row
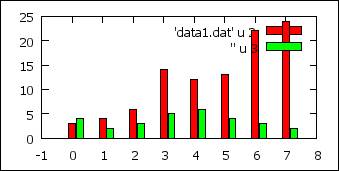
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/histograms.html
Bar chart / histogram 2
p 'data1.dat' u 1:2:($2*0+0.8) w boxes notitle # last column = size of the
boxes = 0.8
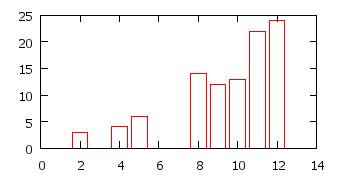
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/histograms.html
Fit
f(x) = a*x + b
# function to fit
fit [1:6]
f(x) 'data1.dat' via a,b # fit in the range
[1,6] only
p 'data1.dat',f(x)
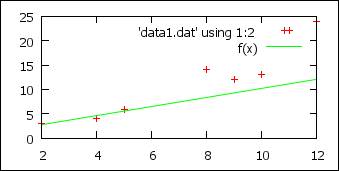
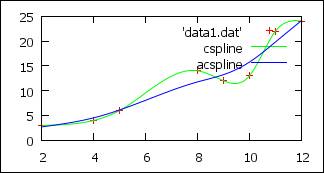
Smooth
p 'data1.dat'\
,'' u 1:2:(1.0)
w lp smooth csplines t
"cspline"\
,'' u 1:2:(1.0)
w lp smooth acsplines t
"acspline" # (1.0) = weight
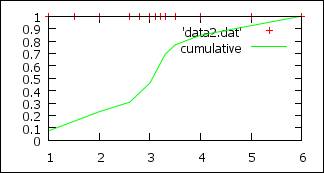
Cumulative
# Useful to plot the cumulative of a serie of random results from probability distribution
# data2.dat
# 1 1
# 3 1
# 2 1
# 3.1 1
# …
p 'data2.dat' ,''
u 1:(1/13):(1.0) w lp smooth cumulative t
"cumulative" # 13 datas, (1.0) = weight
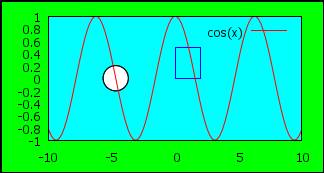
Rectangles, circles, and background
# background
with rectangle
set object 1 rectangle from screen 0,0 to screen 1,1 behind fc rgb "green" # full screen rectangle, behind all other
set object 2 rectangle from graph 0,0 to graph 1, 1 back fc rgb "cyan" fillstyle
solid 1.0 # graph background
set object 3 rect from 0,0 to 2,0.5 fs empty border rgb
"blue"
# small rectangle, empty, border blue
set object 4 circle at -3*pi/2,0. size
1 fs
transparent border rgb "black"
p cos(x)
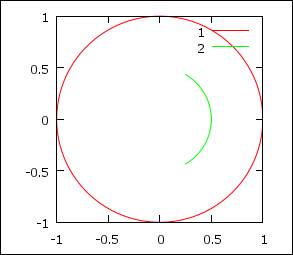
Parametric
set size ratio 1
# size screen x = size screen y
set parametric
# enter parametric : variable t
set trange [-pi:pi]
# set range for parametric
set xrange [-1:1]
# range for x
set yrange [-1:1]
# range for x
fx(t,r,c) = r*cos(t/c)
# function -> x, r = radius, c = to vary parametric range
fy(t,r,c) = r*sin(t/c)
# function -> y, r = radius, c = to vary parametric range
plot fx(t,1,1),fy(t,1,1) t "1",fx(t,0.5,3),fy(t,0.5,3)
t "2" # 2nd
from –pi/3 to pi/3, radius = 0.5
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/param.html
Styles
p cos(x) w l t "import" lc rgb "green" lw 3 # width =3, color = “green”
set style line 1 lc rgb "blue" lw 3
p cos(x) w l t "import" lc rgb "green" lw 3, sin(0.3*x+0.5) w l ls 1
Plot and command window
p cos(x)
# plot cos(x)
plot 'file.dat' e 10
# plot only 1/10 of the points: e=every
p 'data1.dat' u 1:2,'' u 1:3 # '' = same file
set sample 10
# x interval by 10 for function f(x), decrease for more accurate
set
label "test" at first 0,0.5
# can be first, second, graph, screen,
or character
clear
# clear figure
reset
#
reset to default the set
replot
# redo last command plot, reread data
refresh
# redo last command with memory, do nor=t read again data
pause 2
# pause 2 s
Plot window
# Shortcuts:
# space =
from plot window to command line
# g :
toggle grid
# wheel
: translate y
# shift+wheel : translate x
# ctrl+wheel : zoom
# ctrl+shift+wheel: zoom x
bind c 'print "great"'
# shortcut: print “great” when hitting c in plot
windows
pause mouse "Click"
# pause until click on window plot
lower 0
# lower window 0
raise 0
# raise window 0 to the top of the windows
test
#
show possibilities of the terminal
# Mouse
print MOUSE_X
print MOUSE_Y
print MOUSE_X2
print MOUSE_Y2
print MOUSE_BUTTON
print MOUSE_KEY
print MOUSE_SHIFT
print MOUSE_CTRL
print MOUSE_ALT
pause mouse keypress
# pause until key is pressed
print "Keystroke ", MOUSE_KEY, " at ", MOUSE_X, " ", MOUSE_Y
# min max
values for the graph
print GPVAL_X_MIN
print GPVAL_X_MAX
print GPVAL_Y_MIN
print GPVAL_Y_MAX
Terminals
# eps -> latex
set term postscript eps enhance
set terminal
postscript eps enhanced color font 'Helvetica,10'
# set terminal epslatex size 8.89cm,6.65cm color colortext
# http://www.gnuplotting.org/introduction/output-terminals/
# http://www.gnuplot.info/docs/tutorial.pdf
set output "test.eps"
# pdf
set term pdf
set output "test.pdf"
# png
set term pngcairo
set terminal pngcairo size 350,262 enhanced font 'Verdana,10'
set output "fig.png"
#wxt : default windows
set term wxt
set term wxt 0 size 300,200 # window number 0, size (height*width=)
300*200
set output
# to save
and restore previous term
set term push #
remembers the current terminal including its settings
set term pop #
restores it
Strings manipulations
print "A"."B"
# "AB"
graph(n) = sprintf("Title for plot
#%d",n) # function with
C format
p cos(x) title graph(4)
# plot with “title for plot #4”
http://www.gnuplot.info/demo/stringvar.html
http://www.gnuplot.info/docs_4.2/gnuplot.html#x1-7000019
Scripts and Macros
#Write the last two mouse click
positions using a bind to key
bind 5 load 'mouse_keep_1.gnu'
# when pressing ‘5’ in plot window, load macro in the file
and the macro file “mouse_keep_1.gnu” is below. Each time the program is loaded, it will
1. push the last position of the mouse (mouse_x_b,mouse_y_b) to (mouse_x_a,mouse_y_a)
2. push the last click position into (mouse_x_b,mouse_y_b)
3. print the result on the screen
4. same for second axes if they exist.
if(defined(MOUSE_X)) if(defined(mouse_x_b))
mouse_x_a=mouse_x_b;else mouse_x_a=0;
if(defined(MOUSE_X)) mouse_x_b =
MOUSE_X;
if(defined(MOUSE_X)) if(defined(mouse_y_b))
mouse_y_a=mouse_y_b;else mouse_y_a=0;
if(defined(MOUSE_X)) mouse_y_b =
MOUSE_Y
if(defined(MOUSE_X)) print "(",mouse_x_a,mouse_y_a,")"
if(defined(MOUSE_X)) print "(",mouse_x_b,mouse_y_b,")"
if(defined(MOUSE_X)) print "(",mouse_x_a,mouse_y_a,")"
if(defined(MOUSE_X)) print "(",mouse_x_b,mouse_y_b,")"
if(defined(MOUSE_X)==0)
print "MOUSE_X not defined, please click on the graph";
if(defined(MOUSE_X2)) if(defined(mouse_x2_b))
mouse_x2_a=mouse_x2_b;else mouse_x2_a=0;
if(defined(MOUSE_X2)) mouse_x2_b = MOUSE_X2;
if(defined(MOUSE_X2)) if(defined(mouse_y2_b))
mouse_y2_a=mouse_y2_b;else mouse_y2_a=0;
if(defined(MOUSE_X2)) mouse_y2_b = MOUSE_Y2
if(defined(MOUSE_X2)) print
"(",mouse_x2_a,mouse_y2_a,")"
if(defined(MOUSE_X2)) print
"(",mouse_x2_b,mouse_y2_b,")"
With this you can load another macro to plot an arrow between the last two mouse positions:
set arrow from mouse_x_a,mouse_y_a to
mouse_y_b,mouse_y_b
you could use a more direct way using the mouse event with some if/else conditions:
pause mouse "Click"
# pause until click on window plot
Save / load
save 'work.gnu'
# save current session
load 'work.gnu' #
load session
Write to file
command=sprintf("echo %f > toto.txt",MOUSE_X)
# define “echo ‘MOUSE_X’ > toto.txt”
system command
# execute command, here write MOUSE_X in “toto.txt”
print GPVAL_PWD
#
current directory
More complicated examples
You can do « almost » anything with gnuplot.
Online ressources
Documentations
http://www.gnuplot.info/documentation.html
http://www.gnuplot.info/docs_4.4/gnuplot.pdf
Books
FAQ/Questions
http://www.gnuplot.info/help.html
http://www.gnuplot.info/faq/faq.html
http://news.gmane.org/gmane.comp.graphics.gnuplot.user
Links
QIPGraphÓ :
C++ and Excel Interface for gnuplot
http://t16web.lanl.gov/Kawano/gnuplot/index-e.html
http://gnuplot-tricks.blogspot.com/
- go to ~loison/